Crystallization is done by evaporation, where all water evaporates and collects to fulfil the reuse purposes
The addition of acid helps to create a solution so that, when it heats, it can avoid measuring and damaging the heat exchangers. DE aeration is commonly used in it simply to dissolve dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other unconventional gases. The remaining waste from the evaporator to the crystallizer continues to boil all the water until the impurities in the water begin to form crystals and are filtered as solid in ZLD system.
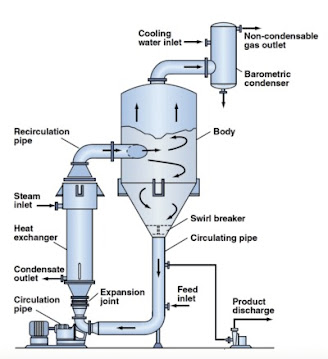
In this process, the solutes must have a melting crystallizer manufacturer crystallization for salt separation curve that will be able to decrease in temperature if the crystallization process uses supersaturation by cooling. The process of supersaturation is achieved by evaporation of solvent only where the solubility depends on the temperature. Crystallization occurs in an evaporator/crystallizer that is forced to rotate, where it generates and add crystals within the mass solution. The crystallizer system is followed by a water extraction device, which separates the salt crystals from the product slurry. The mother liquor is returned to the crystallizer for further concentration.
The evaporator circulation is usually supplied with an external steam heating source due to the high boiling point of the solution at high concentrations. The process of vacuum crystallization involves a combination of evaporation and cooling when the solution is placed under vacuum conditions, as a result of which the solvent suddenly evaporates and cools the solution through an adiabatic process.
There is usually a side opening to facilitate access to the manual extraction of shiny salts. At the end of the cycle, the vacuum is released and the contents of the boiler are removed manually with a scraper blade through one of the front doors. Crystallizers can work well with heat pumps, steam, or hot water. This approach is one of the most common ways of achieving greater industrial efficiency and this process also depends on the properties and characteristics. The crystallization process is not an easy one and is the most important part of producing solid crystals from liquid form. First, the solution is concentrated and later reduced, until the solute concentration is higher than dissolved. As a result, the solute will form pure crystals. The speed at which crystals are formed is known as the crystallization rate.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment